Table of Contents
- Overview
- Frequently Used FMC Terms
- FMC Supported Platforms
- System Requirements (Sample)
- Common FMC Operations
- Troubleshooting Commands
- Useful FMC Resources
- Change Log
- Conclusion
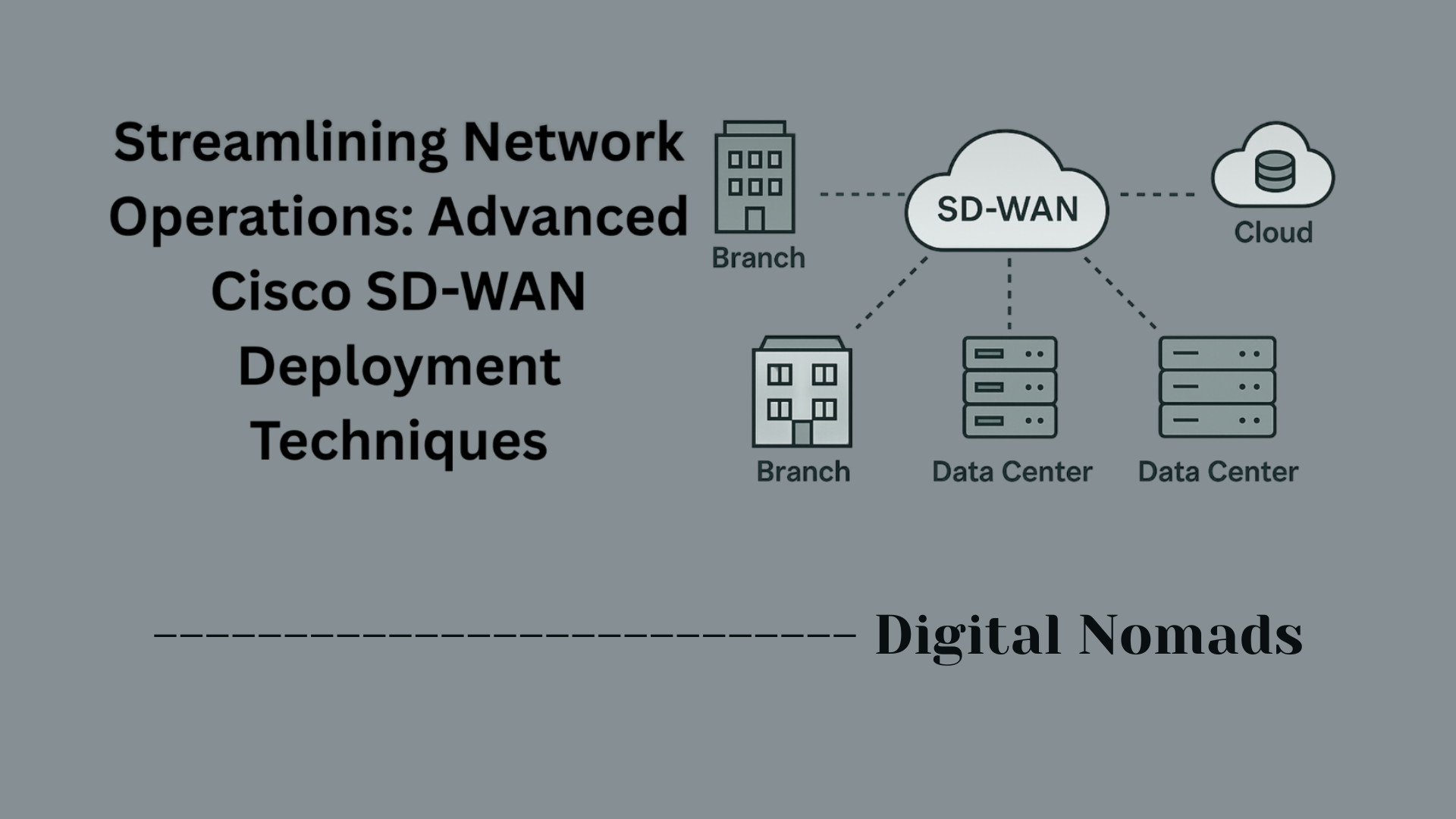
Cisco FirePOWER: Firepower Management Center (FMC) Overview
What is FMC?
The Firepower Management Center (FMC) is Cisco’s centralized platform for managing the entire suite of Cisco Secure Firewall and threat defense devices. It acts as the brain of the Cisco FirePOWER system, providing a single interface to configure, monitor, analyze, and optimize security policies and responses across your network infrastructure.
FMC supports both physical (appliance) and virtual deployments, and manages various Cisco security devices, such as Firepower Threat Defense (FTD) appliances, Next-Generation Intrusion Prevention Systems (NGIPS), and ASA firewalls with FirePOWER services.
Why Do You Need to Know About FMC?
- Centralized Security Control: FMC consolidates management for multiple security appliances into one platform, greatly simplifying network security operations. This reduces the risks associated with fragmented policy administration and human error.
- Unified Policy Management: It enables you to define, deploy, and track security policies—such as access control, intrusion prevention, and malware protection—across all supported devices, ensuring consistent protection.
- Enhanced Visibility and Analytics: FMC provides real-time and historical insight into network traffic, threats, and user behavior, helping security teams quickly identify and respond to security incidents.
- Regulatory Compliance: With robust reporting, auditing, and logging features, FMC supports compliance requirements for security standards and frameworks frequently used in regulated industries.
- Operational Efficiency: Automation of recurring tasks, streamlined workflows, and integration with external systems (e.g., SIEM) all result in less manual effort and faster response times for security teams.
How Does FMC Work?
- Device Management: FMC communicates securely with each managed device, allowing administrators to push configurations, software updates, and fixes from a central console. Devices register with FMC and routinely share operational status and event logs.
- Policy Creation and Deployment: Administrators use FMC’s web interface to create comprehensive security policies—such as access rules, intrusion policies, and network address translations (NAT). These policies are then deployed from FMC to all registered devices with just a few clicks.
- Event Collection and Analysis: All managed devices continuously send event data (such as threat detections, connection logs, and security alerts) back to FMC. The platform aggregates and correlates this data, providing dashboards, customizable reports, and advanced analytics to identify threats and suspicious activity.
- Automated Response and Reporting: Based on the policies and correlation rules defined within FMC, the system can trigger alerts, block traffic, or automate containment actions when an incident is detected. Detailed logs and reports are generated to support further investigation, compliance, or audit requirements.
- Third-Party Integration: FMC can integrate with other security tools and platforms, including SIEM solutions, identity services, and orchestration tools, to enable end-to-end security operations and improved incident response.
FMC is essential for organizations using Cisco’s security stack because it simplifies complex firewall and threat protection tasks, delivers unified visibility, and empowers security teams to defend against evolving network threats with precision and efficiency.
Frequently Used FMC Terms
Get familiar with these essential FMC terms to make working with Cisco’s Firepower Management Center more effective:
- FMC (Firepower Management Center): The centralized management platform for Cisco security appliances, providing unified configuration, monitoring, and reporting for threat defense devices.
- FTD (Firepower Threat Defense): An integrated threat-focused next-generation firewall software that combines Cisco ASA and FirePOWER services, offering advanced threat protection and VPN support.
- Access Control Policy: The ruleset within FMC that defines which network traffic is allowed or denied, controlling security boundaries and user/application permissions.
- Intrusion Policy: A group of settings and rules for identifying, blocking, or alerting on potential network attacks, leveraging deep packet inspection and threat intelligence.
- Event Correlation: The process of linking multiple detected security events to recognize coordinated or complex attack patterns, providing context for analysis and response.
FMC Supported Platforms
The Cisco Firepower Management Center (FMC) can manage a variety of Cisco security devices and platforms, both hardware and virtual. Here are the main supported platforms as of recent releases:
-
Cisco Firepower Threat Defense (FTD) Appliances:
- Firepower 1000 Series (e.g., 1010, 1120, 1140, 1150)
- Firepower 2100 Series (e.g., 2110, 2120, 2130, 2140)
- Firepower 4100/9300 Series (all supported models)
- ISA 3000 Industrial Security Appliance
-
Cisco ASA with FirePOWER Services:
- ASA 5500-X Series (selected models for FirePOWER modules)
- ASA 5585-X with FirePOWER SSP modules
-
Firepower Next-Generation Intrusion Prevention System (NGIPS):
- Firepower 7000/8000 Series (Legacy support in older releases)
-
Firepower Management Center Virtual (FMCv):
- Supported on VMware ESXi, KVM, Amazon AWS, and Microsoft Azure cloud platforms
For the most accurate information, always check Cisco’s official compatibility documentation for your FMC version. New devices and versions may be added or retired over time.
System Requirements (Sample)
Before deploying Cisco Firepower Management Center (FMC), make sure your hardware and software environment meets the minimum requirements for reliable performance. These requirements are a general guideline—always confirm with your version’s official release notes for the latest details.
- CPU: Quad-core processor (2.0 GHz or higher recommended)
- Memory (RAM): Minimum 16 GB
- Disk Space: Minimum 250 GB available storage
- Supported Browsers: Recent versions of Chrome, Firefox, or Microsoft Edge
- Network: 1 Gbps network interface or faster recommended for efficient management communications
Note: Requirements may vary depending on FMC deployment size, type (hardware, virtual, or cloud), and number of managed devices. For production deployments or large-scale networks, consider Cisco’s recommended and “performance optimal” hardware specs.
Common FMC Operations
The Cisco Firepower Management Center (FMC) streamlines complex security administration with centralized control over policy deployment, device health, event analysis, and reporting. Here are the essential FMC operational tasks that security teams regularly carry out:
- Policy Deployment and Management: Create, modify, and deploy security policies (access control, intrusion, malware, NAT, VPN, and more) from a single console. Updates and rule changes are pushed to all managed devices, ensuring consistent protection across the network.
- Device Health Monitoring: Use built-in health modules and dashboards to track the operational status of FMC and all connected security appliances. Monitor hardware/software health, CPU/memory usage, and receive alerts on system issues for proactive maintenance.
- Intrusion Event Analysis and Reporting: Investigate network intrusion events with robust reporting tools, traffic graphs, and incident logs. Analyze threat patterns, view summaries and details of security incidents, and generate scheduled or on-demand reports for compliance and forensics.
- User and Application Traffic Visibility: Gain real-time insights into user activity, applications, protocols, and behavioral trends. This visibility helps enforce compliance and adapt security measures to changing network usage.
- Integration with External Logging and Alerting: Integrate FMC with external systems such as syslog servers or SIEM platforms for centralized alerting, logging, and automated response workflows.
These daily operations enable security teams to maintain a strong security posture through efficient, unified management and continuous visibility into threats and network activity.
Troubleshooting Commands
Effective troubleshooting in Cisco Firepower Management Center (FMC) involves using a set of key CLI commands and scripts. These commands help administrators diagnose issues, gather debug information, and perform basic health checks. Below are some of the most common troubleshooting commands and their uses:
-
system generate-troubleshoot [options]:
Generates a comprehensive troubleshooting bundle with logs and diagnostics. Use
ALLto collect everything or specify types likeNET(network data),SYS(system logs), orVDB(vulnerability database info).
Example:system generate-troubleshoot ALL - show managers: Lists the management centers currently configured, useful to verify connections between devices and FMC.
- show running-config: Displays the current running configuration of the device for quick parameter checks or backup.
-
system support diagnostic-cli:
Enables access to advanced diagnostic commands. Entering this mode allows you to use commands like
ping,traceroute, and variousshowcommands for deeper troubleshooting. - sudo sf_troubleshoot: Generates a troubleshooting file on the FMC that can be provided to Cisco TAC for support.
- manage_procs.pl: A script to restart or reconfigure communication channels between FMC and managed devices, helpful for resolving lost connectivity.
- pigtail: Tails multiple log files in real time, making it easier to monitor logs during troubleshooting sessions.
- ping <IP>, traceroute <IP>: Executes network reachability and path testing from the CLI, verifying connectivity to other devices.
These commands enable administrators to swiftly isolate issues and gather the critical information needed for troubleshooting Cisco Secure Firewall deployments.
Note: Access levels and available commands may vary based on user permissions and software versions. Use caution with advanced scripts and commands in production environments.
Useful FMC Resources
Here are essential resources for getting the most out of Cisco Firepower Management Center (FMC). These links cover official documentation, troubleshooting guides, support channels, and communities to help you with deployment, management, and ongoing operation:
-
Official Documentation Portals:
-
Configuration Guides: Find comprehensive installation, configuration, and administration guides for different versions and deployment types.
Example: Secure Firewall Management Center Administration Guides, Device Configuration Guides, Snort 3 Configuration Guides[1][2][5] -
Release Notes & Upgrade Guides: Always consult release notes when updating FMC software or managed devices.
Example: Firepower Management Center Release Notes (search by version)[1][2]
-
Configuration Guides: Find comprehensive installation, configuration, and administration guides for different versions and deployment types.
-
Best Practices & Troubleshooting:
-
Best Practice Guides: Guides and presentations covering common configuration mistakes, tips, and tricks.
Example: Cisco Community Best Practice discussions and Cisco Live session archives[3] -
Troubleshooting Guides and Knowledge Base: Quick reference for issues, common errors, and troubleshooting workflows.
Example: Cisco Communities “Quick Links” and Troubleshooting TechNotes[7][8][10]
-
Best Practice Guides: Guides and presentations covering common configuration mistakes, tips, and tricks.
-
Official Cisco Support Channels:
- Technical Assistance Center (TAC): For advanced issues, open a TAC case or search the support database for solutions.[10]
- Security Advisories & Notices: Stay updated on patches, vulnerabilities, and security notices related to FMC.[4]
-
Online Community Forums:
- Cisco Community: Peer-to-peer forums for real-world deployment advice, troubleshooting help, and shared experience from other network professionals.[3][8]
- Third-Party Tech Forums: Get broader perspectives and solutions from industry professionals working with FMC in diverse environments.[11][20]
-
Video Tutorials & Playlists:
- Official Cisco YouTube Playlists: Step-by-step deployment, configuration, and feature overview videos.[8]
Tip: Bookmark your version’s documentation and the official Cisco Community for quick access and up-to-date support.
Change Log
This section provides a chronological record of significant updates, enhancements, or corrections made to the blog post or documentation surrounding Cisco Firepower Management Center (FMC). Maintaining a change log helps track improvements for readers and contributors.
| Date | Description |
|---|---|
| 2025-07-15 | Initial creation of the FMC appendix and documentation structure. |
Tip: Update this change log every time you make substantial edits, corrections, or add new sections. This ensures transparency and keeps all readers informed.
Conclusion
Throughout this blog post, we explored the Cisco Firepower Management Center (FMC) and its crucial role in modern network security operations. FMC stands out as the unified management solution for Cisco’s next-generation firewalls, intrusion prevention systems, and advanced malware protection platforms. It provides end-to-end visibility into network activity, devices, threats, and vulnerabilities, allowing security teams to easily manage firewalls, enforce application control, and respond swiftly to incidents—all from a single console.
Key takeaways include:
- Unified Management: FMC centralizes device, policy, and event management, eliminating the complexity and risk associated with managing security policies across separate platforms.
- Exceptional Visibility: With detailed contextual awareness, security teams have real-time insights into users, hosts, applications, files, and threats, empowering them to make informed decisions and fine-tune their security posture.
- Automated Response: FMC streamlines security operations through automated event correlation, dynamic policy recommendations, and remediation capabilities, significantly reducing incident response times.
- Scalability and Integration: Whether you’re managing a handful of devices or hundreds, FMC adapts to a variety of environments and supports seamless integration with Cisco and third-party technologies for broader threat intelligence and workflow automation.
- Continuous Improvement: FMC’s intuitive reporting, behavioral analytics, and ongoing monitoring give organizations the tools to adapt to evolving threats and maintain compliance over time.
In a fast-changing cybersecurity landscape, Cisco FMC equips organizations with the intelligence, control, and operational efficiency needed to stay ahead of threats and safeguard critical assets. Whether you’re a seasoned security professional or just beginning your journey with Cisco’s security ecosystem, mastering FMC is a step toward robust, scalable, and responsive defense.
Thanks for following along, and here’s to stronger, smarter security management! If you have questions or want to dive deeper into any aspect of FMC, feel free to reach out or explore the official Cisco resources linked in our "Useful FMC Resources" section. Stay secure!