Table of Contents
- Overview
- Authentication & Access
- Available Tools & Libraries
- Common Use Cases
- Example Automation Integrations
- Example API Endpoints
- Community and Support Resources
- Best Practices
- Sample Code Snippet (Python)
- Conclusion
Cisco Meraki: APIs and Automation – Overview
What Is Cisco Meraki: APIs and Automation?
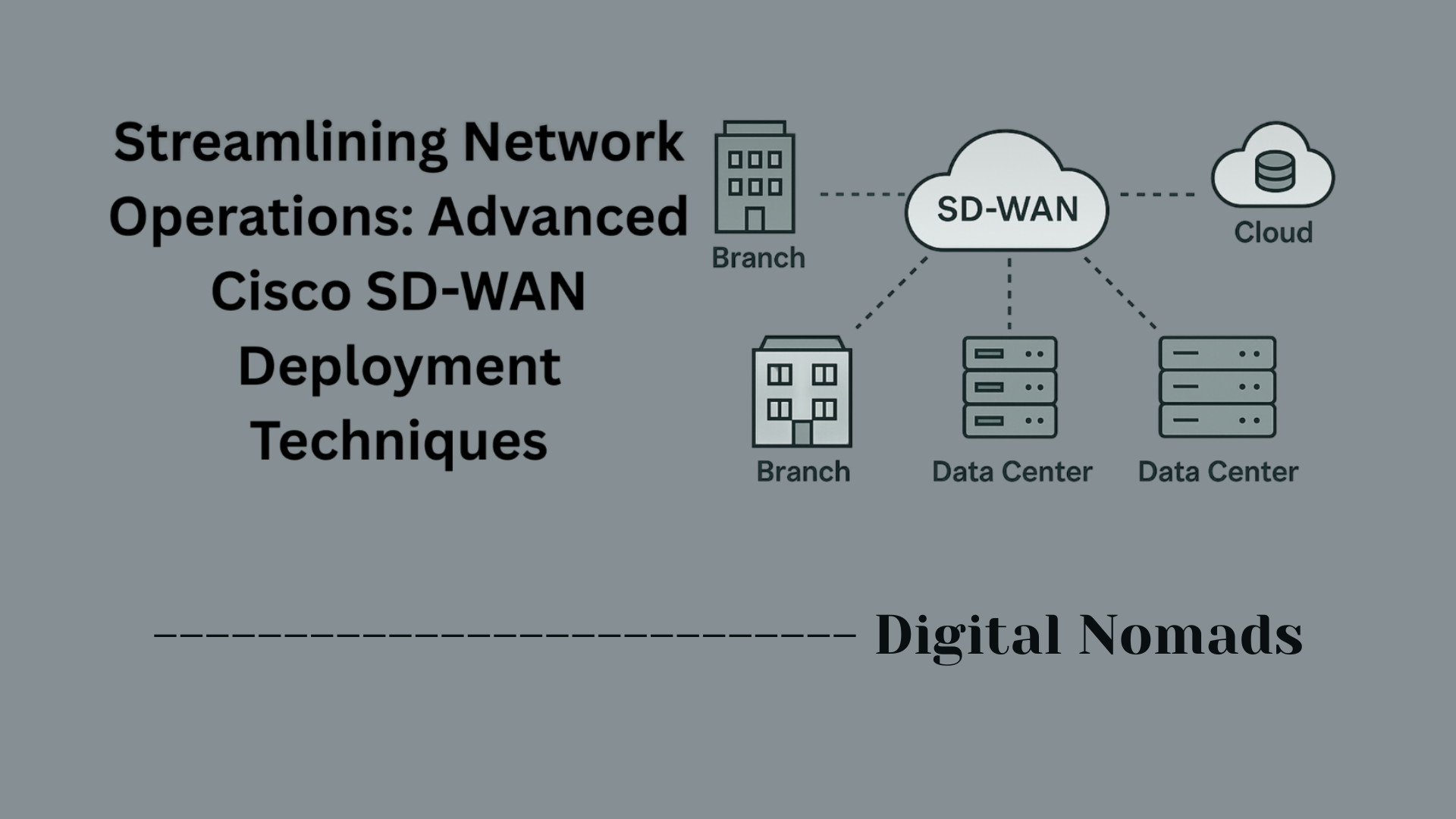
Cisco Meraki offers cloud-managed networking solutions, such as switches, firewalls, wireless access points, and security cameras, all centrally controlled through the Meraki Dashboard. The Meraki API is a set of RESTful interfaces designed to allow programmatic access to this dashboard, empowering you to automate network management, deployment, and monitoring tasks across your entire infrastructure.
APIs and Automation in the context of Meraki mean that instead of configuring each device or network manually through the web interface, you can use software (scripts or external platforms) to handle routine or large-scale operations quickly, accurately, and efficiently.
Why You Need to Know About It
- Operational Efficiency: Automation eliminates repetitive manual tasks, reducing human error and freeing up engineering time for more strategic work.
- Scalability: APIs enable management of thousands of devices or hundreds of customer environments in minutes—enabling rapid provisioning, bulk changes, and network consistency.
- Integration: Automation allows you to link Meraki with other applications and platforms (like SIEM, ITSM, or DevOps tools), creating end-to-end workflows for alerts, tickets, monitoring, and business analytics.
- Agility and Compliance: Consistent, code-driven configuration management ensures networks remain compliant, standardized, and responsive to change, while making it easy to audit and rollback changes as needed.
For network security engineers and operations teams, adopting Meraki APIs is critical to evolving your infrastructure from manual, device-focused management to network-as-code. This approach is essential for large enterprises, MSPs, and anyone embracing “infrastructure as code” or Zero Touch provisioning.
How It Works
- RESTful API Model: The Meraki Dashboard API is accessed over HTTPS, using modern REST principles. Each resource—networks, devices, VLANs, clients, etc.—has distinct endpoints with standard HTTP methods (GET, POST, PUT, DELETE).
- Authentication: Access is secured by API keys, which are generated in the dashboard and mapped to admin permissions. Keys must be included in every API call—ensuring each action is secure and auditable.
- Automation Workflows: You can use official software development kits (SDKs) for Python, JavaScript, and other languages, as well as Postman collections or community scripts, to interact with the API. This enables automation of tasks like device onboarding, firmware upgrades, bulk configuration, compliance checks, and reporting.
- Integration Ecosystem: Meraki API and webhooks make it possible to build highly customized workflows (such as automated alerting, CI/CD infrastructure changes, or dynamic access control) and integrate with third-party platforms or low-code solutions.
- Monitoring and Feedback: API-driven management provides real-time status and analytics, supporting event-driven automation and rapid response to network changes or issues.
In summary, Cisco Meraki APIs and automation tools are the foundation for building secure, scalable, and future-proof network operations. By leveraging these capabilities, organizations move beyond manual processes to achieve true agility, reliability, and innovation in network management.
Authentication & Access
To leverage Cisco Meraki's APIs securely and efficiently, follow these step-by-step guidelines for authentication and access management:
-
Generate an API Key:
Access your Meraki Dashboard and navigate to your user profile. Find the "API & Webhooks" section, then click to generate a new API key. Copy this key and store it securely—treat it like a password. -
Associate the API Key with Permissions:
API keys inherit the permissions of the admin who created them. Ensure your user role only has the privileges you intend to grant API access, and remove unnecessary access when possible. -
Secure Your Credentials:
Never share your API key in code repositories or public forums. Rotate keys regularly, and revoke immediately if a key is lost or compromised. -
Use API Keys in Requests:
For each API call, add your API key to the HTTP headers usingX-Cisco-Meraki-API-Keyas follows:X-Cisco-Meraki-API-Key: YOUR_API_KEY -
Respect Rate Limiting:
Meraki enforces a limit of 10 API calls per second per organization. If you exceed this, you'll receive HTTP 429 errors. Implement retry logic in your automation scripts. -
Audit and Monitor Usage:
Regularly review API usage logs in the Meraki Dashboard for unexpected activity. Limit API key scope and permissions for security.
By following these steps, you maintain a secure and reliable setup for Meraki API-driven automation and integration.
Available Tools & Libraries
Cisco Meraki APIs streamline automation with the support of a rich ecosystem of official and community-built tools. Here’s how to access and use these resources, step by step:
-
Python SDK:
The Meraki Python library wraps the entire Dashboard API and simplifies most operations. Features include automated pagination, logging, error handling, and support for simulation (dry run) modes.- Install with a single command:
pip install meraki
- Import and use it in your scripts to perform API actions quickly.
- Install with a single command:
-
JavaScript & TypeScript SDK:
Developers working in Node.js or front-end environments can use the officially maintained package to make API calls, handle errors, and manage pagination efficiently.
- Install with:
npm install @cisco-meraki/dashboard-api-tools
- Install with:
-
Postman Collections:
Pre-built Postman Collections allow you to test, visualize, and document API endpoints without writing code.- Download and import the Meraki Postman Collection for immediate access to API requests.
- Use built-in environment variables for managing API keys and base URLs securely.
-
Open Source Scripts:
The Meraki community curates numerous ready-to-use Python and Node.js scripts for common automations (like device inventory, network provisioning, audits, and more).- Browse and adapt these scripts for your environment, or contribute your own improvements.
-
Integrations & Utilities:
- Google Sheets add-on: Access API data for reporting and management without coding.
- Node-RED nodes and bots: Create event-driven API workflows visually.
Choosing the right tool depends on your preferred language, skillset, and use case. Start simple with Postman or Google Sheets, or go directly to SDKs and code for seamless workflow integration and advanced automation.
Common Use Cases
Cisco Meraki APIs empower automation across diverse network environments. Here’s a step-by-step look at common, practical use cases:
-
Provisioning Networks and Devices:
Automate creation of organizations, networks, VLANs, SSIDs, and bulk onboarding of devices. This saves hours when scaling client sites or handling multi-site rollouts. -
Bulk Configuration and Change Management:
Apply configuration changes across many networks simultaneously—such as updating firewall rules, group policies, or alert settings—eliminating repetitive manual work. -
Automated Device Deployment:
Claim and assign devices to networks, update firmware versions in batches, and remotely configure equipment before it even arrives onsite. -
Onboarding and Offboarding Users:
Automatically set up equipment and access controls for new users, or revoke access for users leaving, supporting zero-touch teleworker and branch setups. -
Inventory and Asset Management:
Retrieve real-time inventories of hardware, clients, and licenses across all networks for compliance, lifecycle management, and asset tracking. -
Monitoring, Alerting, and Reporting:
Gather network health data, bandwidth statistics, event logs, and create custom dashboards or automated alerts with webhook integration. -
Configuration Drift and Compliance Audits:
Compare live configurations against baselines, detect unauthorized changes, and trigger remediation or notifications if compliance gaps are found. -
Location and Analytics Integrations:
Use camera and Wi-Fi presence APIs to enable location-based apps, crowd analytics, or business intelligence integrations. -
Role-Based Automation and Portals:
Build custom UIs or automation scripts to provide self-service or role-limited operations to teams (e.g., allowing help desk staff to perform device reboots without full dashboard access). -
Integration with SIEM and External Platforms:
Connect Meraki APIs with SIEM solutions for security event ingest, or sync with cloud collaboration and ticketing platforms to drive network-aware workflows.
By adopting these use cases, organizations can improve accuracy, scale operations, and reduce the operational overhead of managing complex networks.
Example Automation Integrations
Integrating Cisco Meraki APIs with third-party automation platforms unlocks advanced orchestration, streamlines network management, and reduces manual effort. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of common integration scenarios:
-
Red Hat Ansible Automation Platform:
Use the official Ansible Collection for Meraki to automate:- Branch network provisioning, deploying configurations to multiple sites automatically.
- Audit and compliance checks by comparing live network settings with best-practice baselines.
- Configuration drift detection and remediation to maintain consistent policies across infrastructure.
- Scheduled Wi-Fi pre-shared key rotation for security, delegating updates to automation instead of manual entry.
-
Gluware Automation Suite:
Gluware leverages Meraki APIs for code-free automation of complex tasks, such as:- Full inventory discovery and dynamic device onboarding.
- Automated configuration audits and drift detection to maintain policy compliance.
- Batch updating settings or deploying new VLANs, SSIDs, or IP helpers across all networks with a few clicks.
-
Workflow Automation Tools (Workato, Mindflow, n8n):
Platforms like Workato, Mindflow, and n8n enable low-code or no-code workflow automation by:- Triggering Meraki API actions based on events, such as new device onboarding or threat detection.
- Integrating Meraki with ITSM, SIEM, or business platforms for ticket creation, reporting, and alerting.
- Automating compliance reports and orchestrating infrastructure changes in response to real-time analytics or incidents.
-
Custom Scripts and Bots:
Utilize open-source Python or JavaScript scripts, or platforms like Node-RED, to:- Automate device reboots, inventory exports, or alert management with fine-grained control.
- Build chatbots or self-service portals that interact with Meraki APIs and empower help desk teams.
Adopting these automation integrations enables organizations to scale operations, improve network reliability, and accelerate change while reducing manual tasks and minimizing risk.
Example API Endpoints
Cisco Meraki APIs provide a modern, RESTful way to automate network management. Here’s a step-by-step reference to some of the most frequently used API endpoints with standard HTTP methods and descriptive tasks:
| Task | Endpoint (relative to Base URI) | HTTP Method |
|---|---|---|
| List Organizations | /organizations |
GET |
| Get Organization Information | /organizations/{organizationId} |
GET |
| Create Organization | /organizations |
POST |
| List Networks in Organization | /organizations/{organizationId}/networks |
GET |
| Create Network | /organizations/{organizationId}/networks |
POST |
| List Devices in Organization | /organizations/{organizationId}/devices |
GET |
| List Devices in Network | /networks/{networkId}/devices |
GET |
| Claim Device to Network | /networks/{networkId}/devices/claim |
POST |
| Update Device Settings | /networks/{networkId}/devices/{serial} |
PUT |
| Get Device Clients | /devices/{serial}/clients |
GET |
| List VLANs in Network | /networks/{networkId}/vlans |
GET |
| Update VLAN Settings | /networks/{networkId}/vlans/{vlanId} |
PUT |
| Get SSID Information | /networks/{networkId}/wireless/ssids |
GET |
| Run Live Tool (e.g., Blink LED) | /devices/{serial}/liveTools/blinkLed |
POST |
Each endpoint is appended to the base URI (https://api.meraki.com/api/v1). Replace {organizationId}, {networkId}, {serial}, and {vlanId} with your actual values. Use these examples as building blocks for powerful Meraki automation workflows.
Community and Support Resources
A strong ecosystem of community, learning, and support resources ensures you’ll never be alone in your Cisco Meraki automation journey. Here’s a step-by-step guide to making the most of what’s available:
-
Join the Meraki Community:
Participate in Meraki’s global forums to get answers, ask technical questions, share use cases, and learn best practices from fellow users and engineers. Leaderboards, trending topics, and monthly recognition encourage knowledge sharing. -
Access the Meraki Developer Hub:
The Developer Hub is the central place for API documentation, SDK/libraries, sample code, learning labs, and interactive sandboxes. It’s ideal for everyone from beginners making their first API call to advanced developers looking for reference guides and OpenAPI specs. -
Leverage GitHub Repositories:
Find or contribute sample code and automation scripts in official and community-run GitHub repositories. These repositories provide hands-on examples for Meraki automation tasks and workflows, speeding up your learning process. -
Explore the Learning Hub and Training:
Take advantage of free, self-paced labs and guided learning paths that cover platform fundamentals, advanced automation, and practical Meraki scenarios. Earn badges and track progress as you build network automation skills. -
Browse Documentation and Knowledge Base:
Cisco Meraki maintains detailed online documentation covering everything from setup guides and API endpoints to best practice recommendations and troubleshooting FAQs. -
Receive 24/7 Technical Support:
Licensed Meraki customers have access to round-the-clock support through the Meraki Dashboard, phone, and web support portals. Cases are managed by dedicated Meraki technical support engineers worldwide. -
Participate in Webinars and User Events:
Join regular webinars for product deep-dives, case studies, and the latest feature releases. Connect with other Meraki users at community events and virtual summits.
By embracing these community and support resources, you’ll accelerate your automation goals, solve challenges quickly, and stay up to date on the latest innovations across the Cisco Meraki platform.
Best Practices
To ensure secure, reliable, and efficient use of the Cisco Meraki APIs, follow these best practices step by step:
-
Secure Your API Keys:
Store keys in secure environments (like environment variables or vaults), never hardcode them in scripts, and rotate them regularly. Revoke keys immediately if compromised. -
Limit API Key Permissions:
Grant keys only the permissions required for their task. Avoid giving unnecessary admin rights to minimize risk. -
Respect Rate Limits:
The API is limited to 10 requests per second per organization. Build retry logic to gracefully handle HTTP 429 errors, and batch operations using action batches to reduce request volume. -
Paginate and Filter Requests:
When retrieving large datasets, use pagination and available filters to avoid pulling excessive data and hitting limits. -
Implement Error Handling:
Always check for and handle errors in responses, including HTTP status codes and API error messages. Implement retries with exponential backoff for transient issues. -
Tag and Identify Automated Requests:
Use unique identifiers or tags in API headers to help identify and audit automation activity. -
Monitor and Audit API Usage:
Regularly review API usage logs for abnormal activity, policy violations, or unexpected volume to detect issues early. -
Document and Modularize Automation Scripts:
Write clear, well-documented code and use modular functions to keep automations maintainable and scalable as your network grows. -
Test in a Non-Production Environment:
Validate new automation scripts in lab or sandbox environments before deploying them to live networks to minimize risk. -
Stay Updated:
Follow Cisco Meraki’s release notes and community updates for changes or new features in the API that may affect your automations. -
Leverage Webhooks:
Use webhooks for real-time event notifications where possible, instead of continuous polling.
Consistently applying these practices will help you maximize automation benefits, safeguard network integrity, and future-proof your Meraki API implementations.
Sample Code Snippet (Python)
Automating network operations with the Cisco Meraki API is straightforward using the official Python SDK. Here’s a clear, step-by-step example to get you started:
-
Install the Meraki Python Library:
Open your terminal and run:pip install meraki
-
Import and Initialize the Dashboard API:
In your Python script, import the library and create a DashboardAPI object using your API key:import meraki dashboard = meraki.DashboardAPI(api_key='YOUR_API_KEY') -
List All Organizations:
Retrieve a list of organizations you have access to:orgs = dashboard.organizations.getOrganizations() print(orgs) # Output the list of organizations -
Create a New Network in the First Organization:
Use the ID from the first organization to create a new network:network = dashboard.organizations.createOrganizationNetwork( orgs[0]['id'], name='Test Network', productTypes=['appliance', 'switch', 'wireless'] ) print(network) # Output network details
With just a few lines of code, you can interact with and automate Meraki deployments. Adapt these snippets for bulk provisioning, configuration, monitoring tasks, and more.
Conclusion
Throughout this blog post, we’ve explored how Cisco Meraki’s powerful APIs can revolutionize modern network deployment, automation, and management. Whether you're managing a single site or thousands of remote branches, automation offers a scalable, repeatable, and secure approach to network operations.
Here are the key takeaways:
- Authentication & Access: Secure API usage starts with managing your API keys responsibly. Always follow permission best practices and monitor API activity regularly.
- Available Tools & Libraries: From Python SDKs and Postman to Node.js and Google Sheets, Meraki’s ecosystem offers tools for both code-savvy engineers and low-code enthusiasts.
- Common Use Cases: Everything from automated provisioning, configuration drift detection, firmware upgrades, to compliance audits can be fully automated using Meraki APIs.
- Example Integrations: Platforms like Ansible, Gluware, n8n, and Node-RED allow you to build robust workflows and automate day-to-day networking tasks effectively.
- API Endpoint Reference: Meraki provides extensive, well-structured endpoints to manage organizations, networks, devices, VLANs, SSIDs, and much more.
- Community & Support: You're backed by a vibrant community, detailed documentation, GitHub resources, and 24/7 support as you extend your Meraki capabilities.
- Best Practices: From reducing rate-limit collisions to securing credentials and building fail-tolerant logic, following best practices ensures your scripts are safe, scalable, and maintainable.
- Code in Action: A working Python example showed how easy it is to list organizations and create networks with just a few lines of code.
Embracing Cisco Meraki's APIs opens the door to true network-as-code—bridging the gap between infrastructure and automation. Whether you’re scripting simple tasks or integrating advanced workflows into your DevSecOps pipeline, Meraki's API-first architecture empowers you to build faster, manage smarter, and scale with confidence.
Thanks for following along. Happy automating!