Table of Contents
- Overview
- API Endpoints and Integration References
- Configuration Templates & Switch Profiles
- Onboarding & API Keys
- SNMP Configuration
- Integrating with External NAC/Security Platforms
- Switch Profile Assignment via API
- Switch Stack Replacement Workflow
- Troubleshooting Tips
- Conclusion
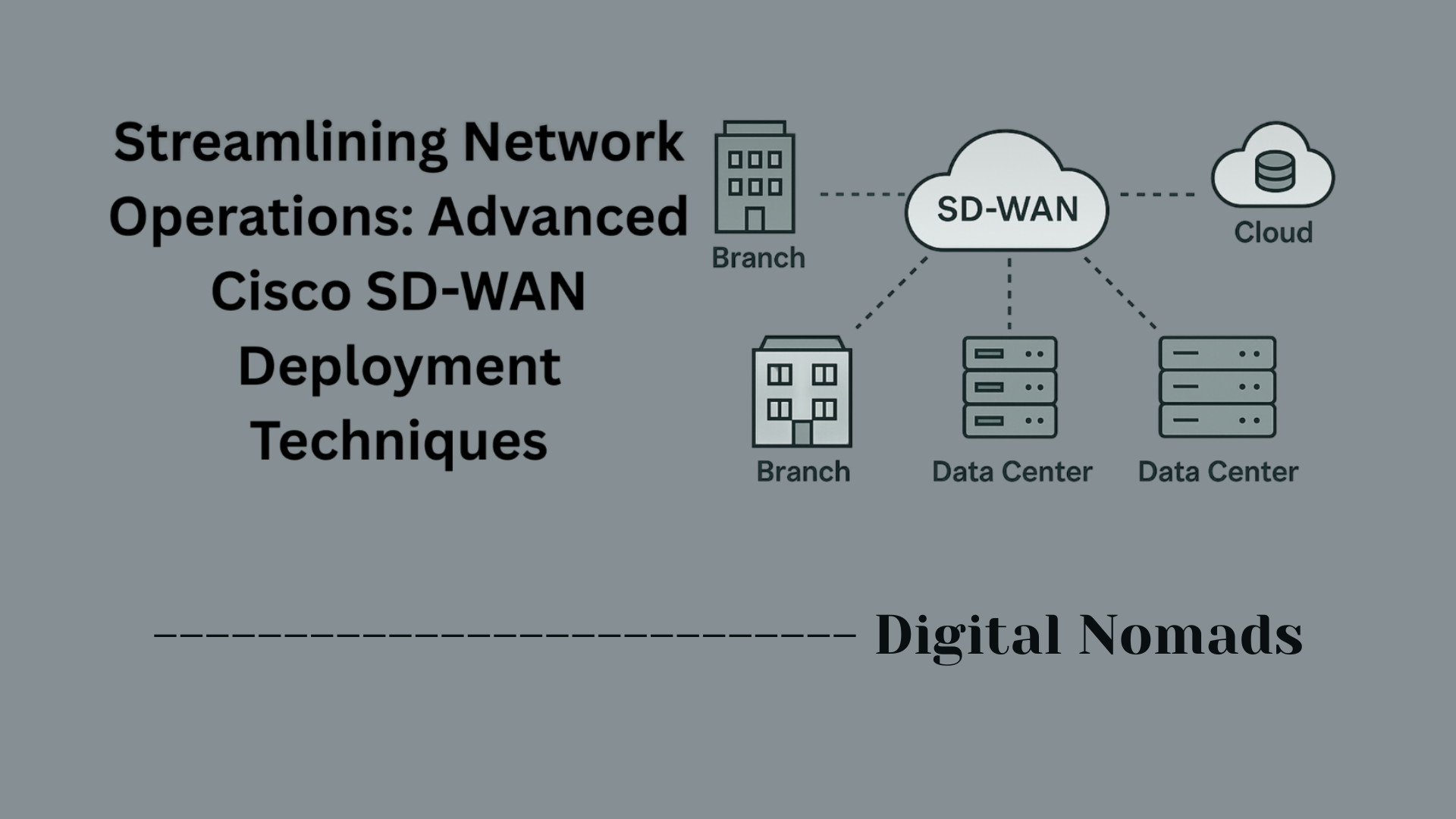
Cisco Meraki: Switches Overview
What Are Cisco Meraki Switches?
Cisco Meraki switches are a family of cloud-managed network switches designed to simplify the deployment, management, and monitoring of modern enterprise networks. Unlike traditional switches, Meraki switches are centrally controlled via the Meraki Dashboard—a user-friendly cloud interface that enables network administrators to manage switches from virtually anywhere.
These switches are available in a variety of models suitable for different environments, ranging from branch offices to large enterprise campuses. They support advanced features including Layer 2 and Layer 3 switching, Power over Ethernet (PoE), stacking, and network access control, all integrated with Meraki's seamless cloud platform.
Why You Need to Know About Meraki Switches
- Centralized Management: The Meraki Dashboard allows IT teams to configure, monitor, and troubleshoot their entire switching infrastructure remotely, reducing the need for on-site visits.
- Scalability: Meraki's cloud architecture supports thousands of switches across multiple locations, making it ideal for organizations with distributed networks.
- Enhanced Security: Built-in features such as anomaly detection, port security, and custom network policies help safeguard against threats and unauthorized access.
- Rapid Deployment: Zero-touch provisioning means switches can be shipped directly to remote offices and come online as soon as they're plugged in and connected to the Internet.
- Integrated Analytics: The Dashboard offers live tools, usage statistics, and event logs to provide end-to-end visibility into network health and performance.
How Meraki Switches Work
- Cloud Management: Each switch securely connects to Meraki’s cloud via an outbound management tunnel using standard HTTPS. No specialized VPNs or hardware controllers are required.
- Configuration & Updates: All switch configuration is done in the Dashboard. Changes are pushed to devices in real-time, and switches receive firmware updates automatically.
- Real-Time Visibility: The Dashboard provides detailed views of switch and port status, allowing administrators to identify bottlenecks, troubleshoot issues, and analyze network usage down to the client level.
- Stacking & Redundancy: Meraki switches support both physical and virtual stacking, enabling multiple devices to function as a single logical unit for ease of management, redundancy, and increased throughput.
- Automation & Policy Enforcement: Administrators can automate common tasks, enforce security policies based on user, device, or application, and segment networks effortlessly.
Cisco Meraki switches are designed to bring ease of use, transparency, and agility to organizations of all sizes, making advanced networking accessible even to smaller IT teams. Their cloud-first approach positions them as a leading solution for businesses seeking reliable, scalable, and manageable network infrastructure.
API Endpoints and Integration References
Meraki switches (MS series) support powerful API capabilities that enable centralized management, automation, and integration with other systems. These endpoints allow administrators to monitor switch port status, configure ports, and gather performance insights.
-
List Switch Ports by Switch:
/api/v1/organizations/{organizationId}/switch/ports/bySwitch
Returns a list of configured ports on all switches in the organization, grouped by switch. -
Switch Port Statuses:
/api/v1/devices/{deviceSerial}/switch/ports/statuses
Retrieves current status, performance, and connectivity data for all ports on a specific switch. -
Switch Port Performance Data:
This data is returned in the response of the statuses API and includes important metrics such as usage, errors, and client connection. -
Uplink Status Across Appliances:
/api/v1/organizations/{organizationId}/appliance/uplink/statuses
Provides real-time data on WAN uplink status for all MX or Z-series appliances in the organization. -
Uplink Usage by Network:
/api/v1/organizations/{organizationId}/appliance/uplinks/usage/byNetwork
Displays data usage trends and WAN traffic analytics over time, grouped by network. -
Generate API Key for Integration:
To use the API, generate a key by going to: Organization > Settings > Dashboard API access, then enable API and generate a secure key. Keys should be treated like passwords. -
Important: All requests must include an
X-Cisco-Meraki-API-Keyheader with your API key and are subject to rate limits.
Configuration Templates & Switch Profiles
Configuration templates and switch profiles dramatically simplify the process of deploying, managing, and updating large fleets of Meraki switches. By applying standardized configuration templates, organizations ensure consistency while still allowing for flexibility when needed.
-
Create a Configuration Template:
- Go to Organization > Configuration templates in the Meraki dashboard.
- Click Create a new template.
- Provide a descriptive name for your template and select the switch model(s) it will apply to.
- (Optional) Copy settings from an existing network or template if you want to reuse existing configurations.
- Click Add to save the template.
-
Customize Switch Templates & Profiles:
- Select your newly created template from the list.
- Navigate to Switching > Configure > Switch templates.
- Click View ports on this switch template to adjust port settings as needed.
- Create Switch Profiles to group switches by model and port configuration. Each profile defines settings for all switches with the same port mix.
-
Bind Networks or Switches to a Template:
- In the configuration template, select Bind networks or Bind switches.
- Choose one or more networks or switches to apply the template settings.
- Click Bind (or Bind to profile if binding individual switches).
- All devices bound to the template will automatically inherit the configuration. Any further changes to the template will instantly update all bound devices.
-
Apply Configuration Changes in Bulk:
- Editing the template or associated profiles will update all bound switches in real time.
- This ensures streamlined operations and eliminates manual errors when deploying updates across different sites.
-
Switch Profile Assignment via API (Advanced):
- List available switch profiles using:
GET /organizations/{organizationId}/configTemplates/{configTemplateId}/switch/profiles - Assign a switch to a profile with:
PUT /networks/{networkId}/devices/{serial}
Include theswitchProfileIdin your API request body.
- List available switch profiles using:
-
Key Considerations:
- Switch templates are ideal for sites with standardized configurations and multiple devices of the same model.
- Site-specific exceptions can still be configured after binding.
- Changing a device’s profile may require manual binding in existing networks.
Onboarding & API Keys
Cisco Meraki switches offer a streamlined onboarding process to bring your devices into cloud management and enable API access for automation and integrations. Follow these steps to quickly onboard switches and generate API keys.
-
Prepare for Onboarding:
- Make sure you have physical or remote access to the switch you want to add.
- Gather credentials and the serial number for each device.
-
Access the Meraki Dashboard:
- Log in to the Meraki Dashboard at dashboard.meraki.com.
- If you do not have an account, create one and set up your organization.
-
Onboard Your Switches:
- Navigate to Organization > Inventory.
- Click Add devices and enter the serial number(s) for the switches you wish to onboard.
- Assign the switches to the appropriate network.
- After onboarding, the switches will appear in the dashboard ready for monitoring and configuration.
-
Enable API Access:
- Go to Organization > Settings.
- Under Dashboard API access, check the box to enable access.
- Click Save Changes if prompted.
-
Generate an API Key:
- Click your username or email in the upper right corner and select My Profile.
- In the API access section, click Generate new API key.
- Copy your API key and store it securely. This key grants administrative access and will not be shown again.
-
Use Your API Key:
- API keys are required for all automated scripts and integrations with the Meraki Dashboard API.
- Keep API keys secure; treat them like sensitive passwords.
-
Key Reminders:
- Only dashboard admin users can generate API keys.
- Each user may have up to two active API keys.
- If a key is lost, revoke and generate a new key from your profile page.
SNMP Configuration
Configuring SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) on Cisco Meraki switches allows you to monitor device status, gather real-time data, and integrate with third-party network management tools. Follow this step-by-step process to set up and secure SNMP on your switches.
-
Access the Meraki Dashboard:
- Log in to the Meraki Dashboard.
- Navigate to Network-wide > Configure > General or Reporting section (depending on your dashboard version).
-
Enable SNMP:
- Scroll down to the SNMP section.
- Select the SNMP version you wish to use:
- SNMP v1/v2c: Simple community-string-based access. Enter a secure community string.
- SNMP v3: More secure—requires a username and password; communications are encrypted.
- Click to Save Changes.
-
Configure SNMPv3 (Recommended for Security):
- Choose SNMP v3 in the configuration panel.
- Set a username and password for authentication and privacy.
- SNMP v3 uses SHA authentication and AES128 or DES for privacy.
-
Set SNMP Access Restrictions:
- For v1/v2c, define allowed IP addresses to limit SNMP access and increase security.
- For v3, this is optional but still recommended as an added security layer.
-
Download Meraki MIB (Optional, for OID lookups):
- In the SNMP settings panel, look for an option to Download MIB file.
- Upload the MIB to your SNMP management system for better object identification and alerting capabilities.
-
Test SNMP Configuration:
- Use tools like
snmpwalkfrom a monitoring server to verify SNMP communication with your switch. - Sample command for v2c:
snmpwalk -v2c -c <community> <switch_ip> - Sample command for v3:
snmpwalk -v3 -l authPriv -u <username> -a SHA -A <authpass> -x AES -X <privpass> <switch_ip>
- Use tools like
-
Configure SNMP Traps (Optional):
- Go to Network-wide > Configure > Alerts.
- Enable SNMP Traps and enter the IP address of your SNMP trap receiver.
- Choose SNMP version (v2c or v3) and provide credentials accordingly.
- Use the Test Trap feature to ensure traps are received successfully.
-
Apply & Review:
- Save all configuration changes.
- Verify SNMP data and alerts are visible in your management system.
- Periodically review SNMP credentials and access lists for ongoing security.
- Tip: SNMPv3 is strongly recommended for security. Always use strong credentials and limit access to trusted IP addresses when possible.
- Note: Each switch must be polled individually; repeaters and devices without an IP address cannot be directly polled with SNMP.
Integrating with External NAC/Security Platforms
Integrating Cisco Meraki switches with external Network Access Control (NAC) and security platforms enables enhanced network security, access enforcement, and automation. Use these steps to connect Meraki switches to popular NAC systems such as Cisco ISE, FortiNAC, or other third-party solutions.
-
Enable SNMP and API Access:
- SNMP is used by many NAC platforms for device discovery and monitoring. Ensure SNMP credentials are configured (preferably SNMPv3).
- Enable the Dashboard API and generate an API key. Both will be required for platform integration.
-
Add Switches to the NAC Inventory:
- Open your NAC/security platform’s management console.
- Navigate to the section for network devices or switches.
- Add each Cisco Meraki switch by specifying its IP address and SNMP credentials.
- For advanced integrations, provide the Meraki API key and organization details.
-
Configure RADIUS Authentication (Optional, for 802.1X NAC):
- In the Meraki dashboard, go to Switch > Access Policies.
- Create or edit an access policy and select 802.1X authentication.
- Enter the RADIUS server IP, shared secret, and specify authentication methods.
- Assign the created policy to the desired switch ports for endpoint verification and access enforcement.
-
Verify Device Visibility and Host Detection:
- Confirm that the NAC solution can discover and profile Meraki switches via SNMP.
- Check for end-host visibility and network mapping to ensure endpoints are being identified and controlled.
-
Configure Enforcement Policies/Groups:
- Within your NAC platform, create enforcement rules or groups based on user roles, device posture, or security policy.
- Link these policies to authenticated devices or endpoints connected to Meraki switches.
- Automate actions such as quarantine, VLAN assignment, or access restrictions when security requirements are unmet.
-
Troubleshoot Integration:
- Review SNMP logs and API response codes for errors or access issues.
- Test authentication flows and endpoint policies to validate enforcement.
- Refer to platform documentation for supported Meraki switch models and integration best practices.
- Tip: Keep API keys and SNMP credentials secure. Regularly update passwords and delete unused integration accounts for better security.
- Note: Integration steps may vary depending on the NAC or security platform in use. Always review vendor documentation for exact workflow details.
Switch Profile Assignment via API
Assigning switch profiles programmatically enhances efficiency and consistency when managing large numbers of Cisco Meraki switches. Follow these step-by-step instructions to assign switch profiles using the Meraki Dashboard API.
-
Retrieve Available Switch Profiles:
-
Use the API endpoint:
GET /organizations/{organizationId}/configTemplates/{configTemplateId}/switch/profiles -
This will return a list of switch profiles, including each profile's unique
switchProfileId.
-
Use the API endpoint:
-
Identify the Target Switch and Network:
- Locate the serial number of the switch you want to assign the profile to.
- Find the network ID (
networkId) where the switch is deployed.
-
Assign the Profile to the Switch:
-
Use the following API call to update device attributes:
PUT /networks/{networkId}/devices/{serial} -
Include the
switchProfileIdin the JSON request body. Example:
{ "switchProfileId": "ID_Number_From_Previous_Step" } - Execute the request. The switch will now be bound to the specified profile and inherit its configurations.
-
Use the following API call to update device attributes:
-
Verify Profile Assignment:
- In the Meraki dashboard, navigate to the switch's details page to confirm the correct profile is assigned.
-
Use API calls to fetch device data and verify the
switchProfileIdconfiguration.
-
Key Best Practices and Notes:
- Only compatible switch models can be assigned to a given profile.
- Profile assignment through the API is ideal for existing networks. For new network creation, enable auto-bind in the dashboard for automatic assignment.
- Manual intervention might be needed for large-scale profile changes if automated methods are unavailable for certain scenarios.
- Always test in a staging environment before updating production devices in bulk.
Switch Stack Replacement Workflow
Follow these steps to safely replace a switch in a Cisco Meraki switch stack, ensuring minimal downtime and configuration consistency:
-
Document the Existing Stack:
- Note the current stack configuration, including stack members, port usage, and uplink connections.
- Capture existing switch and port configurations from the Meraki Dashboard.
-
Schedule Maintenance Window:
- Plan the replacement during a low-traffic period to minimize service disruption.
- Notify stakeholders of the expected downtime.
-
Remove the Old Switch:
- Power down the stack or isolate the switch to be replaced.
- Disconnect the old switch from stack cables and network connections.
- Remove the device from the Meraki Dashboard, and document serial numbers as needed.
-
Add the Replacement Switch:
- Physically install the new switch in the stack position of the old switch.
- Connect stack cables and relevant network uplinks in the same configuration as before.
-
Configure in the Meraki Dashboard:
- Add the new switch’s serial number to the Meraki Dashboard.
- Apply the old switch’s configuration (name, tags, and port settings) to the replacement device.
- Ensure the replacement switch adopts the stack configuration and synchronizes with other members.
-
Verify and Test:
- Check that all stack members are online and recognized in the dashboard.
- Confirm port and uplink statuses, and verify traffic flow through the replacement switch.
- Run validation tests to ensure network connectivity and stack stability.
-
Finalize and Document:
- Update network documentation with the new serial numbers and stack topology.
- Notify stakeholders of completion and normal network operation.
Troubleshooting Tips
Use these step-by-step troubleshooting strategies to quickly resolve common Cisco Meraki switch issues:
-
Check Device Connectivity:
- Ensure the switch has power and is properly connected to the network.
- Look for solid or blinking status lights indicating hardware health and connectivity.
-
Verify Internet Access:
- Log into the Meraki Dashboard and confirm the switch status is ‘Online’.
- If offline, verify upstream connectivity (ISP modem, firewall, or core switches).
-
Check Uplink Configurations:
- Confirm that uplink ports are configured correctly and that ports are not administratively disabled.
- Use the Dashboard's "Tools" section to ping gateway or DNS servers from the switch.
-
Inspect Port Traffic and Errors:
- Go to the individual switch page in the Dashboard and review port statistics.
- Look for CRC errors, dropped packets, or high usage that may indicate physical cable or speed mismatch issues.
-
Review Event Logs:
- Check the switch’s "Event log" in the Meraki Dashboard to track link flaps, STP changes, or configuration errors.
-
Use Cable Test Tool:
- From the Dashboard, run cable tests on suspicious ports to rule out physical layer issues.
-
Validate VLAN and DHCP Settings:
- Ensure ports are assigned to the correct VLANs and that DHCP settings are properly configured for end devices.
- Ensure clients are receiving the correct IP address, subnet, gateway, and DNS settings.
-
Perform Packet Captures (Optional):
- Use the “Packet Capture” tool within Meraki Dashboard to isolate packet-level communication issues between devices.
-
Reboot the Affected Switch:
- If necessary, issue a remote reboot via the Meraki Dashboard to resolve software-based or temporary hardware issues.
-
Contact Meraki Support:
- If issues persist after basic troubleshooting, open a case directly from the Dashboard for expert assistance from Meraki Support.
Conclusion
Throughout this blog post, we’ve explored the key components and workflows that make Cisco Meraki switches such a powerful and user-friendly networking solution. From understanding how to seamlessly replace a switch in a stack to practical, step-by-step troubleshooting guidance, we aimed to empower you with actionable insights for real-world operations.
Here’s a quick recap of the key takeaways:
- Cisco Meraki switches are intuitive, cloud-managed, and ideal for scalable deployments.
- Replacing a switch in a stack involves careful planning, documentation, and synchronization to avoid downtime.
- Troubleshooting your network can be simple and effective when leveraging Meraki Dashboard tools like event logs, cable tests, and packet captures.
With centralized management, robust performance, and powerful built-in diagnostics, Cisco Meraki switches offer a streamlined approach to modern networking.
Thanks for following along! Whether you’re optimizing an enterprise network or setting up a branch office, we hope this guide helps you navigate your Meraki deployment with greater confidence.
Feel free to share this post with your team or bookmark it for future reference — and as always, happy switching! 🚀