Table of Contents
- Overview
- Acronyms and Definitions
- Common Security Features in Cisco Switches
- Example CLI Commands
- Best Practices
- Conclusion
Overview of Cisco Switches: Security Features
What Are Cisco Switch Security Features?
Cisco switches are essential networking devices used to connect multiple devices within a local area network (LAN). To protect data integrity, ensure network availability, and control access, Cisco switches come equipped with a variety of security features. These features help defend against unauthorized access, malicious attacks, and internal network threats by providing mechanisms for authentication, traffic filtering, encryption, and monitoring.
Why You Need to Know About Cisco Switch Security Features
Understanding and implementing Cisco switch security features is critical for anyone responsible for network administration or cybersecurity because:
- Protect Network Integrity: Prevent unauthorized devices and users from connecting to the network.
- Mitigate Common Attacks: Stop threats such as ARP spoofing, IP/MAC address spoofing, rogue DHCP servers, and denial-of-service (DoS) attempts at the switch level.
- Maintain Compliance: Meet regulatory and organizational security policies requiring network access control and logging.
- Secure Management: Protect the devices themselves from being compromised through secure remote management.
- Ensure Business Continuity: Minimize network downtime caused by security breaches or misconfigurations.
In today’s environment of sophisticated cyber threats, neglecting switch security can jeopardize the entire network’s safety and reliability.
How Cisco Switch Security Features Work
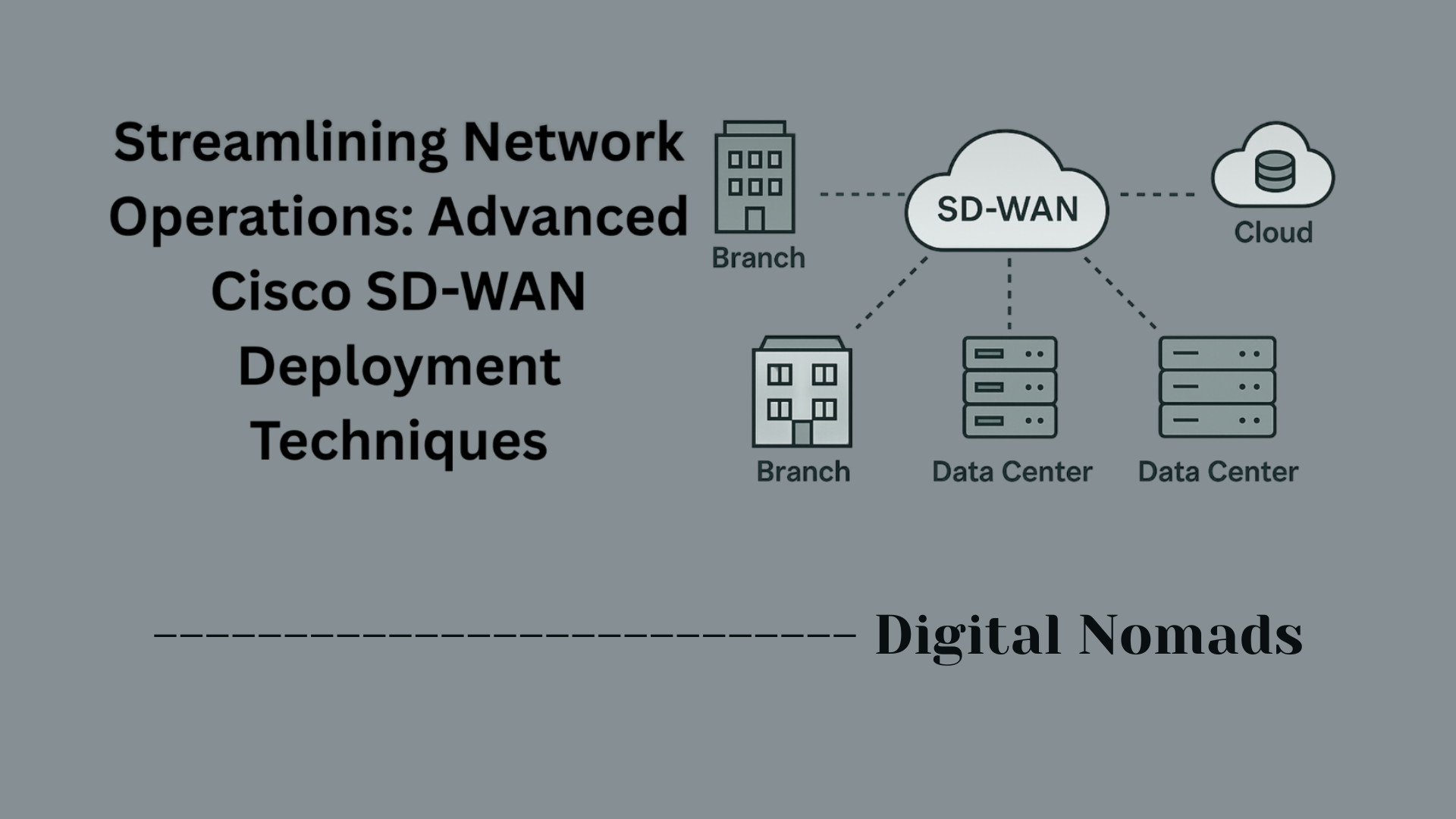
Cisco switch security features operate primarily at Layer 2 (Data Link) of the OSI model but extend to Layer 3 (Network) and management layers depending on the feature. Here’s how they generally work:
- Access Control: Features like port security, 802.1X authentication, and Network Access Control (NAC) control which devices are allowed to connect by verifying device identity and limiting port access to trusted MAC addresses or authenticated users.
- Traffic Filtering: Access Control Lists (ACLs) and private VLANs restrict and segment traffic, allowing only authorized communication paths and reducing the attack surface within the LAN.
- Spoofing and Attack Prevention: DHCP snooping builds a trusted database of legitimate IP-to-MAC bindings to block rogue DHCP servers. Dynamic ARP Inspection uses this data to prevent ARP spoofing. IP Source Guard stops IP spoofing by validating IP and MAC associations.
- Encryption and Secure Protocols: MACsec encrypts Ethernet traffic on link-level connections to protect data from eavesdropping or tampering. Secure management protocols like SSH and SNMPv3 provide encrypted and authenticated communication for network administration.
- Monitoring and Logging: Cisco switches support logging and monitoring of security-related events and can be integrated with network management systems for real-time alerts and audits.
Together, these features create a layered defense approach that strengthens the network at its foundational connection points, making it harder for attackers to penetrate or disrupt operations. Applying these features appropriately and in combination is key to a robust Cisco switch security posture.
Acronyms and Definitions
This section explains the key terms and acronyms you'll encounter when learning about Cisco switch security features:
- AAA (Authentication, Authorization, and Accounting): A framework used to manage user access, verify identities, enforce policies, and track activity across the network.
- ACL (Access Control List): A set of predefined rules that control the flow of traffic to and from interfaces on the switch, based on IP address, MAC address, or protocols.
- DHCP Snooping: A security feature that filters untrusted DHCP messages and helps prevent rogue DHCP servers from handing out IP addresses.
- DAI (Dynamic ARP Inspection): Inspects ARP packets in a network to prevent ARP spoofing attacks, ensuring devices are using legitimate IP-to-MAC address bindings.
- IPSG (IP Source Guard): Blocks traffic on Layer 2 interfaces unless the IP and MAC address information matches what’s learned through DHCP snooping.
- NAC (Network Access Control): Restricts access to the network by enforcing security policies and ensuring that only compliant and authenticated endpoints are granted access.
- MACsec (Media Access Control Security): Provides Layer 2 encryption on Ethernet links to prevent eavesdropping, tampering, and replay attacks on LAN traffic.
- SNMPv3 (Simple Network Management Protocol Version 3): A secure protocol for monitoring and managing network devices, offering authentication and encryption of messages.
- 802.1X: A network access control protocol for authenticating devices and users that attempt to connect to the network.
Common Security Features in Cisco Switches
Cisco switches provide a comprehensive set of security features that help protect network infrastructure against unauthorized access, internal threats, and various attack vectors. Below are some of the most important security features implemented in modern Cisco switches:
- Port Security: Restricts each physical switch port to specified MAC addresses, helping to block unauthorized devices from network access.
- Access Control Lists (ACLs): Filters network traffic by permitting or denying packets based on source/destination IP, MAC address, or protocol. Enhances both Layer 2 and Layer 3 security.
- DHCP Snooping: Inspects DHCP traffic and maintains a binding table to prevent rogue DHCP servers and unauthorized IP address assignments.
- Dynamic ARP Inspection (DAI): Validates ARP packets on the network using the DHCP snooping database to prevent ARP spoofing and man-in-the-middle attacks.
- IP Source Guard: Blocks traffic from untrusted hosts by verifying IP-MAC bindings, making IP spoofing more difficult.
- Private VLANs (Protected Ports): Isolates devices at Layer 2, preventing direct communication between ports in the same VLAN for greater segmentation.
- Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) Security: Features like BPDU Guard and Root Guard protect against malicious or misconfigured devices that could disrupt network topology.
- Storm Control: Prevents broadcast, multicast, or unicast storms by limiting traffic rates, protecting network performance and stability.
- 802.1X Authentication: Provides port-based access control, requiring users and devices to authenticate before accessing the network.
- MACsec (Media Access Control Security): Encrypts Ethernet traffic at Layer 2, preventing eavesdropping and data tampering on wired links.
- SNMPv3 (Simple Network Management Protocol v3): Enables secure monitoring and management of network devices with authentication and encryption.
Many of these features are configurable via Command-Line Interface (CLI) and can be customized to align with organizational security policies. Implementing them systematically is key to robust network defense.
Example CLI Commands
This section provides sample Cisco CLI commands for enabling popular security features on your switches. Copy, edit, and use these as part of your switch configuration process for enhanced security:
-
Enable Port Security:
Switch(config)# interface FastEthernet0/1 Switch(config-if)# switchport port-security Switch(config-if)# switchport port-security maximum 2 Switch(config-if)# switchport port-security violation restrict Switch(config-if)# switchport port-security mac-address sticky -
Enable DHCP Snooping:
Switch(config)# ip dhcp snooping Switch(config)# ip dhcp snooping vlan 10 Switch(config)# interface FastEthernet0/1 Switch(config-if)# ip dhcp snooping trust -
Enable Dynamic ARP Inspection (DAI):
Switch(config)# ip arp inspection vlan 10 Switch(config)# interface FastEthernet0/1 Switch(config-if)# ip arp inspection trust -
Configure 802.1X Authentication:
Switch(config)# aaa new-model Switch(config)# radius-server host 10.1.1.1 key MyRadiusKey Switch(config)# interface FastEthernet0/1 Switch(config-if)# switchport mode access Switch(config-if)# authentication port-control auto Switch(config-if)# dot1x pae authenticator -
Enable MACsec (where supported):
Switch(config)# interface GigabitEthernet0/1 Switch(config-if)# macsec -
Configure an Access Control List (ACL):
Switch(config)# ip access-list standard ALLOWED_HOSTS Switch(config-std-nacl)# permit 192.168.1.100 Switch(config-std-nacl)# deny any Switch(config)# interface FastEthernet0/1 Switch(config-if)# ip access-group ALLOWED_HOSTS in -
Secure Management Access (Enable SSH):
Switch(config)# hostname MySwitch Switch(config)# ip domain-name mydomain.com Switch(config)# crypto key generate rsa general-keys modulus 2048 Switch(config)# username admin privilege 15 secret MySecretPwd Switch(config)# line vty 0 4 Switch(config-line)# transport input ssh Switch(config-line)# login local
Adapt these commands as needed for your environment and specific Cisco switch model. Always reference Cisco’s official documentation before deploying changes in production.
Best Practices
To maximize the security and reliability of your Cisco switches, it’s essential to follow industry-recognized best practices. Applying these recommendations helps safeguard network resources, reduce vulnerabilities, and align with compliance requirements:
- Enable and regularly update security features: Use features like access control lists (ACLs), port security, and 802.1X authentication. Ensure all critical security patches and updates are applied promptly to protect against evolving threats[6].
- Secure management interfaces: Configure SSH (not Telnet) for remote management and use SNMPv3 for encrypted, authenticated network monitoring. Restrict management access to trusted networks only[4].
- Enforce least privilege: Give users and systems only the minimum rights required. Restrict physical, remote, and administrative access to authorized personnel[6].
- Regularly review configurations and logs: Audit switch settings, port usage, and access logs to detect suspicious behavior or unauthorized changes. Automate configuration backups.
- Implement network segmentation: Use VLANs and private VLANs to minimize the blast radius of any security breach by isolating critical systems and user groups.
- Monitor for threats and anomalies: Employ Cisco’s encrypted traffic analytics, Trustworthy Systems capabilities, and threat detection tools as supported by your platform[1][4].
- Educate staff and users: Provide regular training on security protocols and the importance of reporting unusual network activity.
- Document and test disaster recovery plans: Maintain up-to-date network documentation and regularly test backup/restoration processes for switches and configurations.
Adopting these best practices ensures your switch infrastructure remains robust, resilient, and ready to meet modern cyber threats.
Conclusion
In this blog post, we explored the critical security features that Cisco switches offer to protect your network infrastructure. From fundamental mechanisms like port security and access control lists to advanced protections such as DHCP snooping, dynamic ARP inspection, and MACsec encryption, each feature plays an essential role in defending against unauthorized access, spoofing attacks, and other common threats.
Key takeaways to remember include:
- Implementing port security and 802.1X authentication helps tightly control which devices can connect to your network.
- Features like DHCP snooping and Dynamic ARP Inspection safeguard against rogue devices and ensure traffic integrity at Layer 2.
- Utilizing ACLs and private VLANs contributes to granular network segmentation and access control.
- Keeping your switch firmware up to date and securing management access with protocols like SSH and SNMPv3 is critical for operational security.
- Following best practices and regularly auditing your configurations greatly strengthens your overall security posture.
By leveraging these built-in Cisco switch capabilities, network administrators can build a more secure, resilient, and manageable network environment capable of withstanding today’s evolving cyber threats.
Thank you for reading! If you have any questions or want to share your experiences with Cisco switch security, feel free to leave a comment below. Stay secure and happy networking!